Blog Credit : Trupti Thakur
Image Courtesy: Google
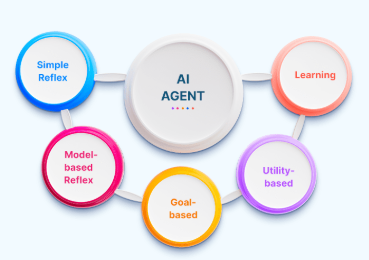
The AI Agents
The landscape of business is set to change dramatically by 2027, with half of the companies adopting generative AI planning to implement AI agents. These intelligent systems will act as smart assistants, capable of managing complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Deloitte forecasts that AI agents will revolutionize industries such as software development, healthcare, and customer service.
About AI Agents
AI agents are autonomous systems designed to interact with their environment. They employ sensors to collect information, a control center for data processing, and effectors to execute actions. As technology evolves, these agents will tackle increasingly sophisticated tasks, including real-time traffic management and personalized education.
Applications Across Industries
AI agents will find applications in various fields. In software development, they can automate coding tasks. In healthcare, they may assist in diagnostics and patient management. In customer service, AI agents can enhance user experience through efficient query handling and support.
Advantages of AI Agents
The introduction of AI agents promises several benefits. They can bridge skills gaps by performing specialised tasks. Their ability to process information rapidly enables them to solve complex problems at scale. This can lead to increased productivity and innovation across sectors.
Potential Risks and Concerns
Despite their advantages, AI agents pose risks. Technical issues such as errors and security vulnerabilities are prevalent. Ethical concerns arise regarding decision-making without human oversight. Additionally, there are fears of job displacement and excessive reliance on AI technologies.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, a new frontier is emerging that promises to revolutionize the way we work and interact with technology.
Imagine you’re taking a break from work, driving to your vacation destination. The weather turns, which lowers the ambient temperature, and increases the volume of traffic.
Your car’s infotainment system has already assessed this new data, so it turns up the heating, reroutes you to quieter roads and suggests a lunch spot where you can sit out the storm.
By 2027, Deloitte predicts that half of companies that use generative AI will have launched agentic AI pilots or proofs of concept that will be capable of acting as smart assistants, performing complex tasks with minimal human supervision.
On the verge of this technological leap, it’s important to understand what AI agents are, their potential impact, and how to navigate the associated risks.
In collaboration with Capgemini, the World Economic Forum has published a new white paper, Navigating the AI Frontier: A Primer on the Evolution and Impact of AI Agents, which explores the capabilities and implications of AI agents, to provide stakeholders with a better understanding of how these systems can drive meaningful progress across sectors.
What are AI agents and how do they work?
AI agents, or ‘agentic AI’, are autonomous systems that sense and act upon their environment to achieve goals. A slew of tech companies are developing AI agents and they’re poised to transform industries and redefine productivity.
Microsoft, IBM, and others have made significant strides, while OpenAI is set to launch an AI agent codenamed ‘Operator’ in January, that will have agency to perform tasks such as coding and booking travel.
Cognition Software launched ‘Devin’ in March 2024, an autonomous software engineer capable of performing complex programming tasks based on natural language prompts.
Investors have recognized the potential of AI agents, pouring more than $2 billion into start-ups focusing on enterprise applications in the past two years. This influx of capital and innovation is driving rapid advancements in the technology.
An AI agent is effectively comprised of several core components:
- The user input or instructions from the human
- The environment within which it operates, which can be physical or digital
- Sensors, through which it perceives its environment
- A control centre, which involves complex algorithms and models
- Percepts – the data inputs it receives about its environment
- Effectors – the tools it uses to take actions, which could be robotic arms or commands sent to other software systems.
- Actions, which represent the alterations made by effectors.
The control centre of advanced AI agents manages the flow of information between user inputs, decision-making and planning, memory management, access to tools and the effectors of the system, enabling action in digital or physical environments.
As the technology evolves, we can expect to see more sophisticated multi-agent systems (MAS) capable of distributing tasks and collaborating on complex problems.
For example, in a smart city, a multi-agent system (MAS) would manage traffic flow in real time, using vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enabling vehicles to interact with other vehicles, pedestrians and road infrastructure.
We will also see greater integration of multimodal data analysis, allowing agents to interpret and produce various types of data, including text, voice and video, as well as industry-specific applications tailored to unique sector needs.
What are the benefits of AI agents?
As AI agents become more capable at reasoning, planning and self-checking, they will be able to carry out tasks beyond the skill sets of users, such as specialized coding, or take on more tedious tasks quickly and at scale.
In a world of talent scarcity, AI agents can help to close skills gaps in various industries, where human expertise is lacking or in high demand.
Greater autonomy allows AI agents to tackle open-ended, real-world challenges from scientific discovery, to improving supply chain efficiency and enabling physical robots that can manipulate objects and navigate physical environments, according to Navigating the AI Frontier.
The report includes five real-world applications of AI agents in sectors from software development and education, to finance, customer service and healthcare, such as enhancing fraud detection, personalizing learning and improving diagnostics and patient treatment.
What are the risks with AI agents and how can they be addressed?
Despite their potential, AI agents pose certain risks around technical limitations, ethical concerns and broader societal impacts associated with a system’s level of autonomy and the overall potential of its use when humans are removed from the loop.
Technical risks include errors and malfunctions and security issues including the potential for automating cyberattacks. The autonomous nature of AI agents raises ethical questions about decision-making and accountability, while there are also socioeconomic risks around potential job displacement and over-reliance and disempowerment.
Harnessing the benefits of AI agents while mitigating risks will depend on the context of the specific environment of the agent and its application.
These are just a few of the measures that organizations should consider in addressing the risks of AI agents:
- Improving the transparency of agents and implementing “human-in-the-loop” oversight, enabling agents to work autonomously while human experts review decisions after they’ve been made.
- Establishing clear ethical guidelines that prioritize human rights, privacy and accountability is an essential measure to ensure that AI agents make decisions that are aligned with human and societal values.
- Prioritizing data governance and cybersecurity before deploying AI agents.
- Implementing public education and awareness strategies is essential to mitigate the risks of over-reliance and disempowerment in social interactions with AI agents.
The rise of AI agents is not just a technological shift; it’s a transformation in how we conceptualize work and human-machine collaboration. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI agents, and by implementing thoughtful strategies for their deployment, businesses can position themselves to harness the full potential of this groundbreaking technology while mitigating associated risks.
As we move forward, it will be crucial to maintain a balance between embracing innovation and ensuring responsible implementation. The future of work is being reshaped by AI agents, and those who adapt wisely will be best positioned to thrive in this new landscape.
Blog By : Trupti Thakur
18
DecThe AI Agents
Dec 18, 2024Recent Blog
The TechKritiApr 26, 2025
India’s First Quantum Computing VillageApr 24, 2025
India’s Achievement In QKDApr 22, 2025
The V2G TechnologyApr 21, 2025
Country’s Specific Domain By GoogleApr 19, 2025




